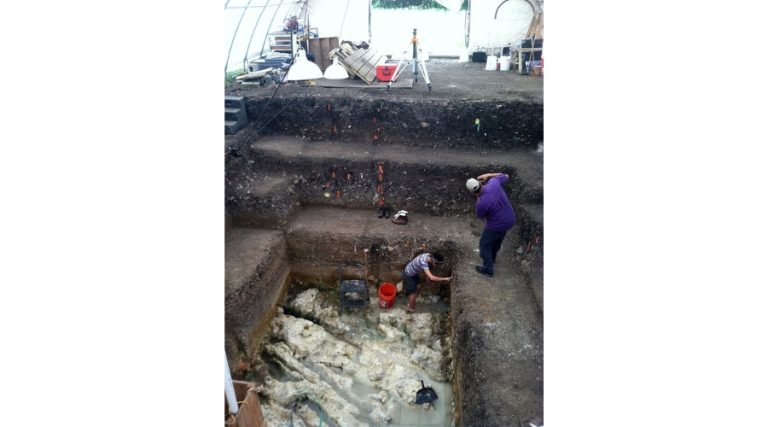
Texas is the location of one of North America’s most significant archaeological discoveries, with evidence of human presence dating back around 16,000 years. Hidden in the Texas Hill Country, this site preserves ancient artifacts and clues about early inhabitants who crafted tools and left traces of their daily lives.
The Gault Site stands out in the field of archaeology for its age and the unique insights it offers into the continent’s distant past. For those interested in prehistory, this location provides a direct connection to some of the continent’s earliest residents, highlighting how Texas plays a crucial role in expanding our understanding of human history in North America.
About The Gault Site
Located in Central Texas within the Edwards Plateau, the Gault Site is a key archaeological area near Buttermilk Creek. Its limestone-rich landscape has preserved extensive material evidence from some of North America’s earliest inhabitants, with artifacts dated through methods such as optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) to over 16,000 years ago.
Key Features:
- Geology: The area’s geology, particularly its limestone layers, has contributed to excellent preservation of ancient tools and remains.
- Artifacts: Items recovered include stone tools, remnants of daily life, and traces of habitation by prehistoric peoples.
- Research Significance: Considered one of the most important archaeological discoveries in the region, it provides valuable insights into ancient cultures and migration patterns.
Visitors and researchers continue to uncover new findings, highlighting the Gault Site’s ongoing importance.
Timeline and Importance of the Gault Archaeological Site
View this post on Instagram
What Sets the Gault Site Apart?
The Gault Site stands out as one of North America’s richest sources of information about ancient human societies. Located in Central Texas, it offered an environment ideal for continuous human use, with dependable water, abundant chert (a type of flint perfect for making tools), and shelter.
Excavations uncovered sediments packed with artifacts, which suggested that the area was not merely a stopping point for passing groups, but probably supported hunter-gatherer communities over thousands of years.
Archaeological teams have recovered more than 2.6 million artifacts here. This collection includes stone tools, chert flakes, expertly crafted projectile points, and rare incised stones showing geometric or abstract patterns.
These decorated stones add a layer to our understanding, revealing an early interest in symbolic or spiritual expression. The most famous artifact group, the Clovis points, exemplifies sophisticated stone tool technology, though discoveries at Gault also include even older projectile points and blades.
What fundamentally changed archaeological debates about early human migration was the recovery of artifacts in distinct layers beneath the Clovis level. These pre-Clovis artifacts, identified using dating methods like OSL, provided evidence for human presence in the area at least 2,000 years before the Clovis culture’s well-documented occupation.
This finding was key in challenging the long-held “Clovis First” model and prompted a reevaluation of the peopling of the Americas.
Table: Highlights of Gault Site Artifacts
| Artifact Type | Association | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|
| Clovis Points | Clovis culture | Fluted design, advanced projectile technology |
| Pre-Clovis Tools | Pre-Clovis period | Older stone tools, blades below Clovis level |
| Chert Flakes | Various | Evidence of toolmaking on-site |
| Incised Stones | Prehistoric cultures | Abstract carvings, early art/symbolism |
The Gault Site’s Impact on North American Archaeological Studies
From its initial excavation by J.E. Pearce and later Thomas Williams, through continued work by researchers like Clark Wernecke, the Gault Site has grown into a central point in American archaeology.
The site’s complexity and depth provided an opportunity to track changes in stone tool assemblages over thousands of years, yielding insight into the shifting lifeways and skills of early human inhabitants.
Excavations in the 1990s and 2000s by the Texas Archaeological Research Laboratory and the Gault School of Archaeological Research deepened the understanding of this site’s significance.
Researchers systematically traced the layers of human occupation, revealing diverse Paleoindian and pre-Clovis artifacts. This careful stratigraphic work enabled archaeologists to build precise chronologies of migration and settlement.
Findings at the Gault Site have informed theories about how people first arrived in North America and dispersed across the continent. The wide range and immense quantity of artifacts make it possible for scholars to reconstruct daily life, migration routes, and adaptation strategies of early hunter-gatherers, as well as their symbolic and technological innovations.
Ongoing research efforts not only shed light on North America’s earliest inhabitants but also help protect and interpret the site. Its listing on the National Register of Historic Places underscores its value as a historical and scientific resource.
The Gault Site continues to serve as an anchor point for archaeological research and education in understanding the peopling of the Americas.
Activities and Highlights
Visitors can schedule a guided tour led by experts familiar with the site’s archaeological work. These tours provide a close look at remarkable discoveries, such as ancient stone tools and engraved artifacts, while guides offer insights into how people lived in this area thousands of years ago.
For those interested in practical experiences, the Gault School at times offers hands-on workshops. Participants can try activities like stone tool-making or learn about excavation methods used by archaeologists, giving them a sense of what fieldwork involves.
Popular Options:
- Guided tours with archaeologists
- Viewing historic artifacts and unique finds
- Occasional interactive workshops and special events
- Opportunities to learn about excavation techniques
| Activity | Description | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Guided Tours | Explore the site with an expert | By appointment |
| Artifact Viewing | See flint tools and carved stones | Part of guided tours |
| Workshops/Events | Hands-on archaeology demonstrations | Offered occasionally |
It’s recommended to check the organization’s website or call for up-to-date scheduling before visiting, since all visits are coordinated around active research.
Essential Visitor Information
View this post on Instagram
Directions and Site Access
The archaeological site managed by the Gault School is found in the Texas Hill Country, roughly 40 miles north of Austin and near Florence. The entrance is marked by a distinctive stone monument at 3433 FM 2843, Florence, Texas 76527.
Since the property is privately owned, visitors are allowed only on guided excursions arranged through the Gault School of Archaeological Research or in collaboration with partners such as the Texas Archaeological Research Laboratory or Texas State University.
Getting There:
- From Austin, travel north on I-35 toward Florence.
- Look for FM 2843 and the marked entrance.
- Advance booking is required for entry.
Visiting Schedule and Guided Experiences
Public access to the Gault Site is organized exclusively through scheduled group tours, led by experts from the Gault School or sometimes in conjunction with university research teams.
Tours are typically offered on the second and fourth Saturdays each month; these dates may be adjusted depending on ongoing fieldwork or seasonal factors. Each excursion lasts about two hours and provides insights into the site’s significance and current research.
- Tours must be booked in advance
- Visit the official Gault School website for reservations and up-to-date scheduling
- Group sizes may be limited for safety and research preservation
Admission Fees and Group Rates
Admission is tiered by age and educational purpose, enabling different groups to visit:
| Category | Price |
|---|---|
| Adults (13 and up) | $20 |
| Children (ages 9–12) | $10 |
| Young Children (8 and under) | Free |
| K-12 Classes & Educators | Free |
For school and field trip arrangements, educators can contact the Gault School directly. Tour fees help support the Prehistory Research Project and site conservation managed by both the Gault School and its university collaborators.
What Visitors Should Prepare
Exploring the Gault Site involves walking outdoors in a rural Texas setting, so preparation is key. It is advisable to wear weather-appropriate clothing and sturdy shoes suitable for uneven terrain. Consider bringing:
- Comfortable walking or hiking shoes
- Hat and sunscreen for sun protection
- Personal water bottle
Additional recommendations may be provided upon booking. Checking the day’s forecast and dressing accordingly will help ensure a comfortable tour for all visitors.
Local Activities and Attractions
Exploring Georgetown
Georgetown‘s picturesque downtown square offers boutique shops, art galleries, and locally owned cafes. The Williamson County Museum is a highlight for visitors interested in learning more about regional history and culture. Walking tours of the historic area and seasonal festivals provide opportunities for a lively and educational afternoon.
Notable Stops:
- Historic courthouse
- Local bakeries and restaurants
- Antique shops
Discovering Inner Space Cavern
Inner Space Cavern, just outside of Georgetown, is known for its ancient rock formations and fascinating cave tours. Tours are available for different activity levels, from easy walks to more adventurous routes. The site shares insights into Texas’s prehistoric geology and the animals that once roamed the area.
| Tour Type | Duration | Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Adventure Tour | 1.5 hours | Moderate |
| Hidden Passages | 1.5 hours | Easy |
| Wild Cave Tour | 2-3 hours | Challenging |
Outdoor Fun at Lake Georgetown
Lake Georgetown is a local favorite for nature lovers and families. The shoreline provides designated picnic spots, well-maintained hiking and biking trails, and swimming areas. Clear signage marks several short and long hikes suitable for different ages and abilities.
Popular Activities:
- Birdwatching
- Kayaking and canoeing
- Shoreline fishing
Visiting Austin
Austin sits under an hour’s drive south and is known for a wide range of attractions including music venues, food trucks, and outdoor parks. Visitors can catch live performances, enjoy barbecue at established institutions, and take relaxing walks along Lady Bird Lake.
Museums and cultural sites in the city provide deeper context on Central Texas history.
Austin Attractions Table:
| Attraction | Type |
|---|---|
| Lady Bird Lake | Outdoor |
| Live Music Venues | Entertainment |
| Texas State Capitol | Historic |
| Barbecue Restaurants | Dining |
Experience Balcones Canyonlands Nature Preserve
Just west of Georgetown, Balcones Canyonlands National Wildlife Refuge offers quiet trails through oak-juniper woodlands. Hikers are rewarded with panoramic Hill Country views and a chance to spot rare bird species, including the endangered golden-cheeked warbler. It’s a fitting location for those seeking peace away from busy city life.
- Recommended Trail: Rimrock Trail
- Wildlife Viewing: Spring and early summer
Additional Visitor Resources
For more information about tours, schedules, and special events, it is recommended to consult the Gault School of Archaeological Research’s website at gaultschool.org. Staff offer assistance for accessibility needs, large group bookings, and field trip arrangements.
Local museums such as the Bell County Museum and Williamson County Museum provide rotating exhibits on archaeology and Texas heritage. Travelers interested in broader prehistoric studies may appreciate research connections to sites like Monte Verde for further context.
Helpful Links:
- Official site: Gault School of Archaeological Research
- Local museums for expanded learning opportunities
- Area visitor centers for up-to-date event calendars