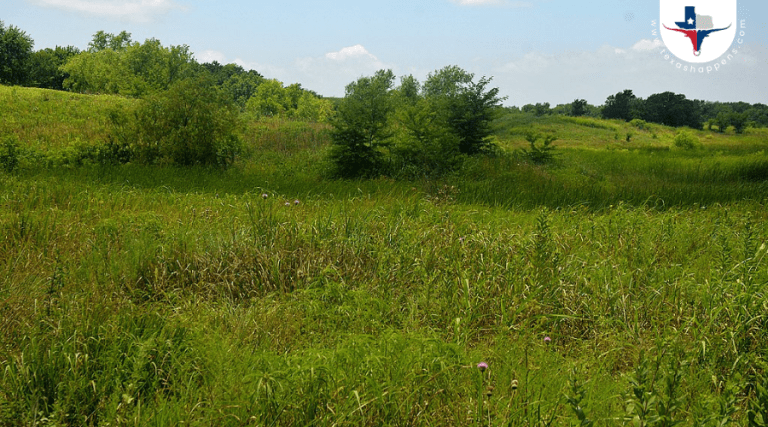
Wilafa, Texas Blackland Prairie, Clymer Meadow Preserve, County Road 1140, Hunt County, Texas, USA (24 June 2021), CC BY-SA 4.0
In the domain of Texas’s diverse soils, Houston Black Soil stands out as a significant and unique type. You’re looking at soil that’s rich in clay and known for its distinctive dark color. This soil is not just any ordinary dirt; it has characteristics that make it highly productive for agriculture. Its clay content gives it a remarkable ability to retain moisture, which is essential in supporting crops like cotton and corn.
This soil type supports a host of native plants and contributes to the biodiversity of the region. It also helps in carbon sequestration, which is crucial in mitigating climate change. So, when you look at Houston Black Soil, you’re seeing more than just soil; you’re witnessing an ecosystem that’s integral to the environment and economy alike. Its characteristics and ecological roles make it indispensable.
Geographic Distribution
This region stretches from the Red River in the north down to San Antonio in the south. The prairies are part of a larger land formation known for its rich, fertile soils. This specific type of soil has developed over thousands of years, making it ideal for agriculture, particularly cotton farming. The rolling prairies and gently sloping hills contribute to the unique distribution of Houston Black Soil in this area.
Soil erosion plays a significant role in this. Over time, wind and water erosion have shaped the landscape, redistributing the soil and affecting its depth and fertility across different areas. Erosion can be both a challenge and a benefit, as it can lead to soil loss in some parts while enriching others.
Key Physical Properties
Color
- Dark Hue: The soil’s black-to-dark gray color is due to its high organic matter content, making it one of the richest soils in Texas.
Texture
- Clay Content: Houston Black Soil has a high clay content, which gives it a fine texture. The clay particles are small and tightly packed, influencing water retention and soil structure.
- Shrink-Swell Capacity: One of its most notable properties, Houston Black Soil, expands significantly when wet and contracts when dry. This unique characteristic can cause visible cracking during drought conditions.
Depth
- Deep Profile: This soil type often extends several feet below the surface, providing a deep root zone for crops and plants.
pH Levels
- Alkaline Nature: The soil’s pH is typically in the range of 7.5 to 8.5, making it slightly to moderately alkaline. This can influence the availability of certain nutrients and requires careful management for optimal agricultural use.
Soil Composition and Structure
Having investigated the geographic distribution of Houston Black Soil, it’s significant to examine its composition and structure. You’ll find that this soil is primarily made up of clay, specifically a type called “Vertisol.” This clay-rich composition is essential because it directly impacts soil fertility. The abundance of clay particles helps in retaining crucial nutrients, making the soil fertile and ideal for agriculture.
When you dig into the structure, notice how tightly packed the particles are. This compactness aids in moisture retention, a critical characteristic for supporting plant growth, especially in Texas’s varied climate. The soil’s ability to hold water means that crops can thrive even during periods of limited rainfall.
You should also pay attention to the organic matter found within Houston Black Soil. Though not overly abundant, the organic content contributes to its fertility and improves nutrient availability. The soil’s structure, with its fine particles, also facilitates the slow release of nutrients to plants, ensuring a consistent supply over time.
Historical Significance
Houston Black Soil not only improves agricultural productivity but also holds a rich historical narrative that reflects Texas’s evolution. When you investigate its past, you uncover its role in shaping the cultural heritage of Texas’s communities, particularly during periods of significant transformation, such as the Mexican-American War, which set the stage for agricultural growth and land development.
Historically, this soil was a foundation for cotton farming, making it a cornerstone of Texas’s agricultural economy. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, vast fields of cotton stretched across the Blackland Prairie, largely due to this soil’s remarkable fertility. You can trace the rise of cotton plantations and the development of railroads that transported produce, all intertwined with the Houston Black Soil.
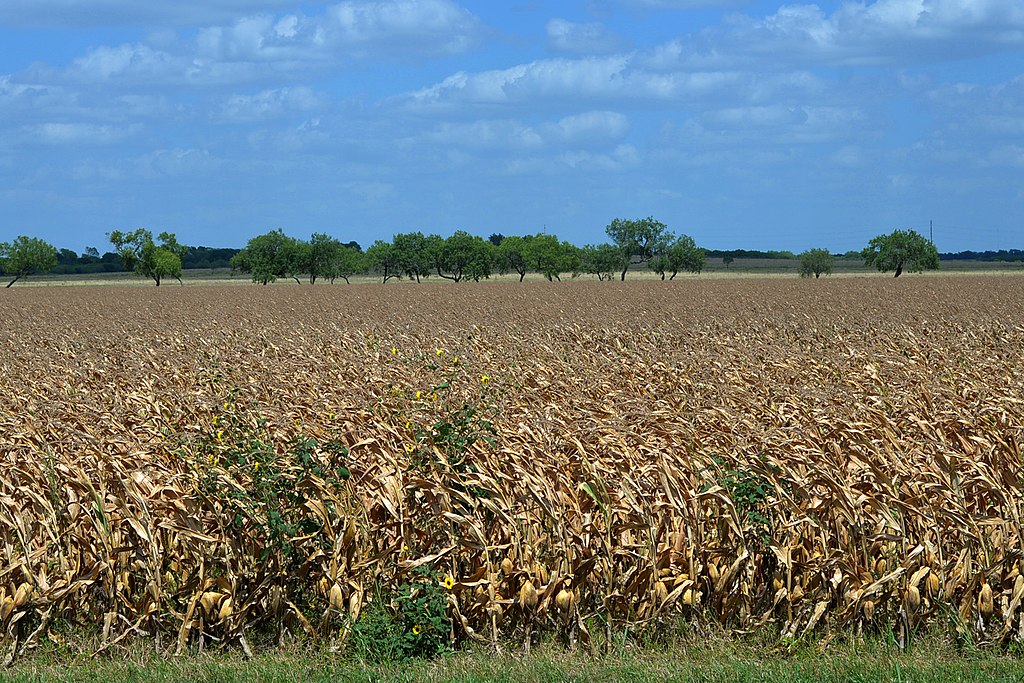

Wrapping Up
Houston Black Soil is a natural treasure that defines the Texas landscape. With its rich fertility, unique shrink-swell properties, and historical significance, it stands out as one of the most distinctive soil types in the United States. While it presents challenges, its contributions to agriculture, ecology, and culture make it an irreplaceable resource.