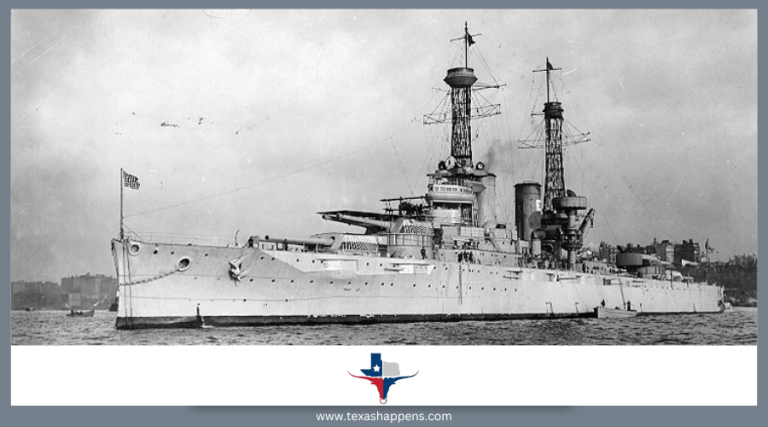
The USS Texas, now a revered landmark, is stationed at the San Jacinto battlefield near Houston. Known as Battleship Texas, its legacy stretches over a century, with two American battleships bearing the name and serving prominently in the U.S. Navy.
As the last surviving dreadnought that served in both World War I and World War II, it played a pivotal role in key naval engagements and technological advancements.
Historical Background

Commissioned in 1914, Battleship Texas was the second ship named in honor of the U.S. state of Texas. As part of the New York-class battleships, it was designed to be a formidable force with its powerful 14-inch guns and heavy armor. During its early years, it participated in training exercises and showed the flag in goodwill missions, establishing itself as a significant asset to the U.S. Navy.
It was primarily involved in convoy escort duties, protecting merchant ships from German U-boat attacks in the North Atlantic. Its presence ensured the safe passage of vital supplies and troops, contributing significantly to the Allied war effort.
Key Battles and Missions
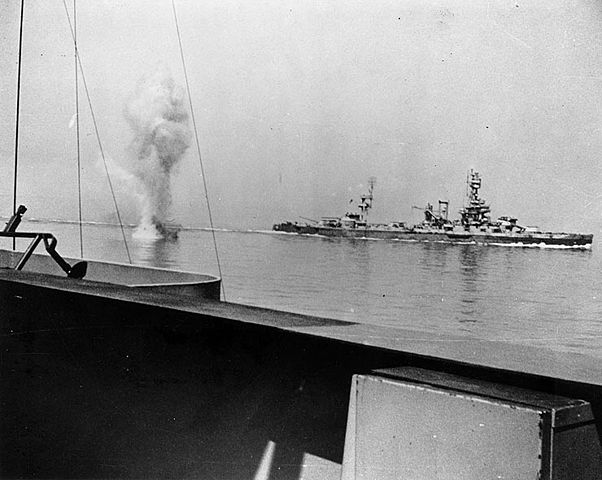

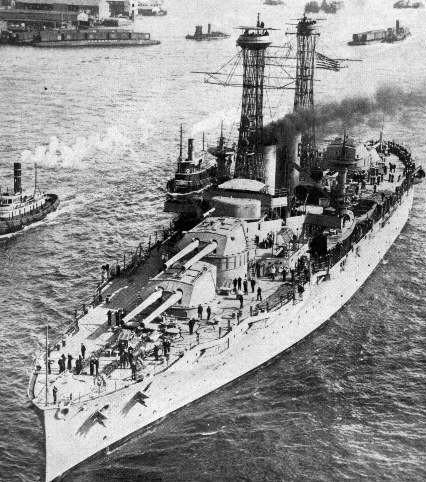
During World War II, Battleship Texas was actively involved in several key battles and missions that underscored its strategic importance. It provided crucial naval gunfire support during the North African invasion, Operation Torch, in 1942. In 1944, it played a significant role in the Normandy Invasion (D-Day), bombarding German defenses at Omaha Beach and supporting ground troops as they advanced inland. Later that year, Texas participated in the Battle of Cherbourg, where its accurate and powerful shelling helped to neutralize heavily fortified German positions.
After World War II, the Texas was decommissioned and given to the state of Texas. It is now preserved as a historical monument near the San Jacinto battleground, where Texas secured its independence from Mexico in 1836. This site, located about 20 miles east of Houston, serves as a reminder of the vessel’s distinguished service.
The custodian of the battleship is the Texas Department of Parks and Wildlife, ensuring ongoing maintenance and preservation. Over the years, the Texas has undergone various restoration projects to maintain its condition and historical value. Today, it serves as a museum ship, attracting thousands of visitors who come to learn about its history and the brave sailors and marines who served aboard.
The Texas is particularly noteworthy for its numerous innovations in naval warfare. It was among the first vessels to feature significant advancements in gunnery, radar, and aviation. The ship’s main armament included 14-inch guns and advanced anti-aircraft measures, making it a formidable force in any naval engagement.
Battle Engagements
The battleship’s involvement in critical operations, such as the North African landings and the Battle of Cherbourg, demonstrated its versatility and effectiveness in combat. Its contributions to naval warfare were recognized with several battle stars, emblematic of its commendable service record.
- World War I: Participated in the North Sea and was at the German High Seas Fleet’s surrender.
- World War II:
- Atlantic: Played a prominent role on D-Day, supporting the Normandy landings at Omaha Beach.
- Pacific: Supported critical operations like the battles of Iwo Jima and Okinawa.
Primary Innovations:
- Gunnery: Introduction of advanced fire-control systems.
- Radar: Early adoption of air search radar technology.
- Aviation: Integration of aircraft catapults and floatplanes for reconnaissance.
Contributions to Major Allied Victories
Battleship Texas’s contributions were pivotal to several major Allied victories. Its firepower and resilience during the Normandy Invasion helped secure the beachhead, facilitating the liberation of Western Europe from Nazi occupation. Additionally, its involvement in the invasions of Iwo Jima and Okinawa provided critical support for the successful assaults on these heavily defended islands. Throughout these operations, Texas’s ability to deliver sustained and precise bombardment was instrumental in weakening enemy defenses and paving the way for Allied advances.
Transition to a Training Vessel
After World War II, Battleship Texas transitioned from active combat duty to serve as a training vessel. This new role involved educating and training naval personnel in various aspects of naval warfare and operations. Its rich combat history and advanced technology made it an ideal platform for hands-on training, helping to prepare new generations of sailors for future challenges.
Decommissioning Process

The decommissioning process of Battleship Texas began in 1948, marking the end of its active service. Stripped of its armaments and combat equipment, the ship was retired from the fleet and slated for preservation. Recognizing its historical significance, efforts were made to preserve Battleship Texas as a museum ship. In 1948, it was turned over to the State of Texas to be maintained as a public memorial, and by 1949, it was permanently anchored at the San Jacinto Battleground State Historic Site, where it remains a powerful symbol of naval heritage and history.
Current State and Ongoing Restoration Projects
Battleship Texas, now a revered museum ship, continues to be a focal point for preservation and education. Despite its age, ongoing restoration projects are dedicated to maintaining and restoring the ship to its former glory. These efforts include structural repairs, hull preservation, and the refurbishment of its interior spaces.
Conclusion
It is a museum ship that offers educational programs and tours to the public. The efforts to preserve this historic battleship are supported by various organizations, donors, and volunteers who recognize the importance of its legacy.
The Battleship Texas Foundation plays a key role in maintaining the vessel’s condition and promoting its historical significance. Through restoration initiatives and community engagement, the foundation helps keep the memory of the Texas alive for future generations.
The story of the USS Texas is not just a tale of a ship; it is a chronicle of the sailors and marines who served aboard and the pivotal moments they shaped in history.