The weather in Texas has a significant role in shaping the state’s unique character and how people go along in their way of life. To avoid harm and prepare yourself for dangerous weather events, familiarity with its weather patterns, seasonal changes, and climate zones is important.
Rising sea levels, warmer temperatures, droughts, and hurricanes are just a few of the threats to consider in context of the state’s varied topography and climate zones. Let’s explore the climatic and changing seasons that occur across the State.
Geographical Factors
The State of Texas is located in the southern region of the United States. It borders Mexico to the south. The state is known for its varied geography that includes coastal plains, rolling hills, prairies, mountains, and deserts. Following are some geographical factors that influence its weather.
Location and Topography
Texas is the second-largest state in the US covering a massive area of 268,596.5 square miles. The state shares borders with New Mexico, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana, and the Gulf of Mexico. While Texas boasts 3,700 streams and 15 rivers, it has no large natural lakes. The highest point in Texas is Guadalupe Peak, which rises 8,749 feet above sea level, and the lowest point is at sea level in the Gulf of Mexico.
With a landscape that varies from southeast coastal plains to central hill country, and from northwest prairies and low mountains to the Davis, Santiago, and Guadalupe mountain ranges of the Rockies in the west, the landforms of this state are incredibly diverse.
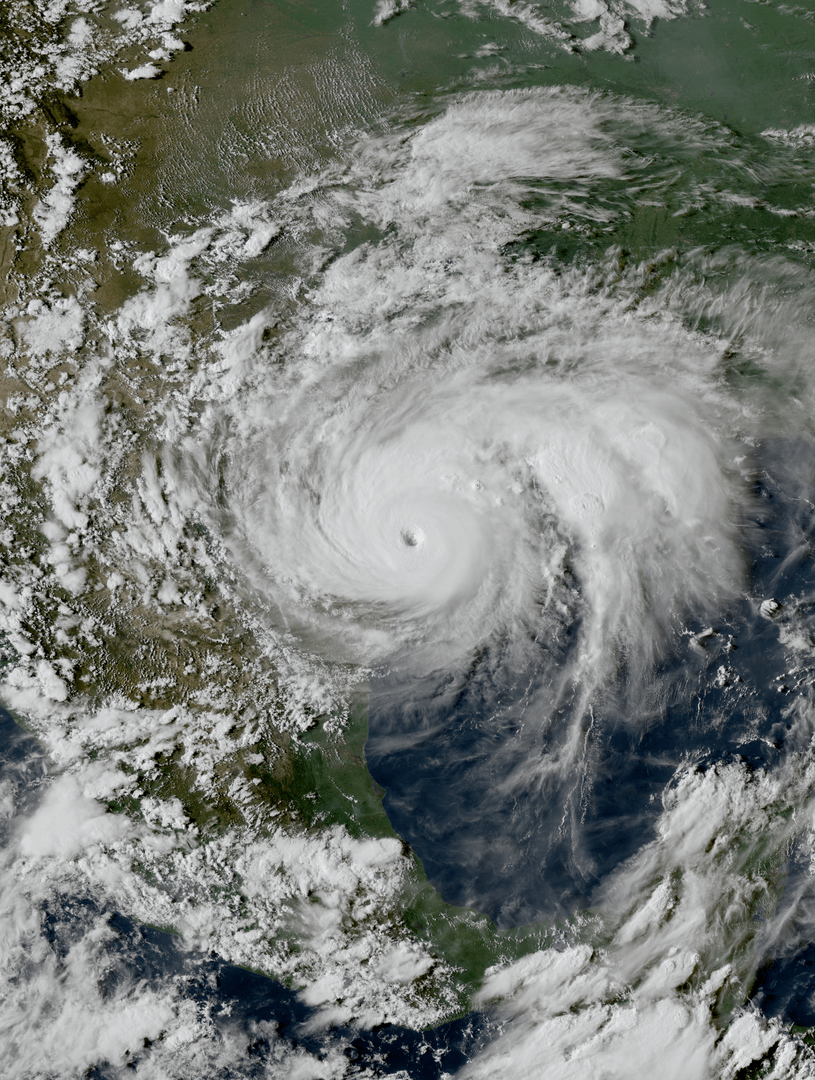
Coastal Influences and Hurricanes
Texas is vulnerable to tropical storms, including hurricanes due to its location along the Gulf of Mexico. Since 1980, Texas has been hit by 81 tropical or subtropical cyclones, with hurricane season running from June 1 to Nov. 30. In 2017, Hurricane Harvey caused extensive flooding and damage in Houston and other parts of Texas. This was also declared as a national emergency for the country as it caused statewide loss of life, power, and communication.
Climate Zones Within Texas
Texas can be divided into four climatic zones: the Coastal Plains, the North Central Plains, the Great Plains, and the Mountains and Basins. The western region of Texas is an arid desert, while the eastern parts are subtropical and humid.
That being said, the city with the best weather in Texas is considered to be Fort Worth with warm summers and mild winters, where the average temperature remains between 37°F to 97°F with rain of about 37 inches yearly. However, two important aspects about Texas include the fluctuating temperature as well as the rainfall patterns. Texas’s climate can be unpredictable, with weather patterns changing rapidly.
Seasonal Variations
The climate of Texas is notoriously unstable, and the state experiences substantial seasonal changes. Below is a detailed explanation of each season’s conditions.
Spring
The bluebonnets of Texas are only one of the many beautiful wildflowers that bloom in the Lone Star State each spring. However, severe weather such as thunderstorms, hail, and even tornadoes are common in the spring as well. The month of May marks the beginning of the rainy season, and the transition from cold winter air to warm spring air can lead to dangerous weather. The average daily temperatures during the Spring season vary from highest 70-80°F (21-27°C), while the average lowest temperature is around 50-60°F.
Summer
Heat waves and droughts in the summer in Texas can make life difficult. Summers in the state are typically quite hot and humid, with highs reaching or even exceeding 100 degrees Fahrenheit. The average high temperature for the season is around 95.5°F. Furthermore, summer drought conditions have worsened, making 2022 the eleventh driest year in the last 128 years.
Fall
The leaves change colors and during the fall with hurricanes being a concern in Texas. The weather is ideal for enjoying the outdoors, with average high temperatures of 78 degrees and lows of 66 degrees. In October and November, the leaves begin to turn brilliant shades of orange, red, and yellow. On the other hand, August is historically the month when most hurricanes make landfall.
Winter
Although the state is better known for its hot summers, Texas winters can also get very harsh. Northern and southern parts of the state, however, might have significantly differing average annual temperatures. Temperatures in the 60s and 70s are normal during the winter in the Rio Grande Valley of southern Texas. Snowfall in Texas can be anywhere between 5 and 20 inches depending on the location. In 2021, a devastating winter storm had taken place in Texas, leading to significant damage, water shortages, power outages and other disruptions..
Extreme Weather
Severe weather is nothing new for the state of Texas. Texans need to be ready for a wide variety of natural disasters from heat waves and droughts to hurricanes to tornadoes and thunderstorms.
Severe Thunderstorms and Tornadoes
Even though severe thunderstorms and tornadoes can happen at any time of the year in Texas, spring is the month when they occur most frequently. In Southeast Texas, there are between 50 and 60 thunderstorms per year, with severe storms. A total of 160 tornadoes hit Texas in 2022, which is a shockingly huge number, while 49 of those occurred in North Texas.
Floods and Flash Floods
Flash floods pose a significant risk to residents, particularly in the state’s central and western regions. There are storms that move slowly as well as storms that move in clusters over the same area. The torrential rainfall of hurricanes and tropical storms can all contribute to flooding. One of the most recent flooding occurred in October 2021 as heavy rains caused flooding in parts of Central Texas including many places of Austin, causing loss of life and property.
Heat Waves and Droughts
Texas has a history of severe droughts, including the Dust Bowl of the 1930s and the drought of the 1950s. The 2011 drought was also extremely damaging to Texas, with 97.5 percent of the state experiencing drought at some point.
As early as late March 1981, the state of Texas experienced 100-degree weather, and on June 28, 1980, the state recorded its warmest summer temperature of around 117 degrees (Wichita Falls). Similar cases emerged in recent times too as Texas experienced severe drought in many parts of the state in 2021. Water restrictions were imposed because crops were failing. Meanwhile, heatwaves have strained the state’s power grid several times. They have also caused massive wildfires in Houston, one of the most interesting cities of America.
Climate change is expected to increase both the frequency and intensity of difficulties. Let’s examine the present climate change trends in more detail:
Climate Change Trends
The coast of Texas is experiencing a faster rise in sea level than normal because of climate change. The primary cause of this is the rising sea levels and faster melting of ice sheets and glaciers. It is forecasted that a large portion of the Texas coast may experience a two to five-foot rise in sea level if the oceans and atmosphere continue to warm. Bird and fish species that rely on tidal wetlands are particularly vulnerable to the effects of rising sea levels, which threaten coastal wetlands, beaches, and public access.
Impacts on Texas’s Weather Patterns and Ecosystems
Frequent drought and rising temperature trends are anticipated to have an adverse effect on the agricultural sector of Texas. Hotter weather causes the kettle to eat less, grow more slowly, give less milk, and harm their health. The same happens with other animals including chicken, goats, and sheep.
Reduced water availability is a problem for ranchers and farmers that irrigate crops, causing output to drop by as much as half in some lands. For the young, the elderly, the ailing, and the poor, hot days can be particularly harmful.
Steps Being Taken to Mitigate and Adapt to Climate Change
The following are the most important steps taken by Texas toward a more sustainable and resilient state:
The Zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions Trio proposes that Texas phase out its use of fossil fuels and increase its use of renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and nuclear power. It will assist in better human health as well as boost air quality.
Through the installation of weatherization materials and education, the Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP) assists low-income households in lowering their energy usage and energy costs. The WAP reduces greenhouse gas emissions and helps low-income households financially by encouraging them to consume less energy by funding them to increase efficiency.
Tree planting, restoring wetlands, and building green spaces are all examples of Green Infrastructure solutions that can lessen the severity of climate change’s adverse effects, such as heat waves, floods, and droughts, which will contribute to the overall enhancement of life in Texas.
The Climate Resilience Action Plan for Austin, Texas, evaluates the effects of extreme weather and lays out ideas for long-term planning to help the city become more prepared for the effects of climate change. This proposal will help Texas cut down on the monetary, human, and ecological toll that severe weather takes on the state.
Understanding and Preparing for Texas’s Climate
To stay informed about weather conditions in Texas, there are many forecasting tools and resources available. The methods for forecasting include persistence, climatology, sky observation, barometer, nowcasting, forecasting models, analogue, and ensemble forecasting.
Emergency Preparedness
Emergency preparedness is crucial to minimize the impacts of extreme weather events. Some resources that can help prepare for emergencies include:
- Bobcat Guardian: A free app for Texas State University students and staff members that creates a safety network, allowing guardians to check their status and contact University Police with their GPS location during emergencies.
- Emergency Supply Kit and Go-Bag: Ready.gov’s recommendations on building a self-sufficient emergency supply kit that lasts for at least three days during disasters.
- Standard Response Protocol: A standard plan of action for community members to stay safe during emergency situations using four response actions: lockout, lockdown, evacuation, and shelter.
Tips for Staying Safe
- Follow weather forecasts and advisories closely.
- Have an emergency kit prepared with food, water, and other essential supplies.
- Know the evacuation routes in your area.
- Follow the advice of local authorities and emergency management agencies.
Conclusion
The varied landscape and climate zones of Texas mean that each season brings its own set of difficulties. Extreme weather events, such as floods, droughts, and storms, are becoming more frequent, making it more important than ever to keep up with the latest information and take preventative measures. Staying safe and reducing the effects of severe weather can be achieved in Texas through the use of forecasting tools, emergency preparedness services, and widespread public awareness.