The Reynosa and McAllen region is a vibrant and populous area situated along the US-Mexico border. This dynamic region comprises the metropolitan areas of Reynosa and McAllen, along with their surrounding suburbs, bridging the two nations with its unique geographical and cultural blend.
On one side of the border lies Reynosa, a bustling city in the Mexican state of Tamaulipas, seated proudly on the southern bank of the Rio Grande. Directly across this mighty river to the north is McAllen, Texas. Together, they form a lively urban area, housing approximately 2.5 million residents, making it the third-largest population center on the US-Mexico border. The McAllen–Hidalgo–Reynosa International Bridge, which spans the Rio Grande, links Reynosa to Hidalgo and McAllen in Texas.
Join us as we take a closer look at what makes this region a unique and important part of Texas.
Historical and Cultural Background
The Reynosa McAllen region, known as the Borderplex, is a significant area along the Mexico-U.S. border. It comprises the city of Reynosa in Mexico’s Tamaulipas state and McAllen in Texas, U.S. This area, notable for its rapid growth, is the largest and third most populous on the U.S.-Mexico border with a population of approximately 1.5 million people.
Reynosa’s Historical Roots
Reynosa, founded in 1749, was part of Spain’s efforts to colonize the Mexican interior. The city was originally positioned near the Rio Grande but was relocated in 1802 due to flooding. It became a site of early rebellion against Spanish rule in 1810. The founding of Reynosa and similar towns along the Rio Grande was pivotal for the Spanish colonial expansion in the region, with missions and ranch settlements forming vital components of this effort by the mid-1750s.
McAllen’s Development
McAllen’s history began quite differently. Around 1903, the area was mainly scattered ranches. The arrival of the St. Louis, Brownsville, and Mexico Railway in 1904 marked a turning point. John McAllen and his son James donated land for the railway, leading to the formation of the McAllen Townsite Company and the establishment of McAllen in 1905.
Initially slow to grow, the community saw a significant boom during the 1910s, with rapid development in agriculture and infrastructure. This period also marked the challenging transition from a Hispanic-dominated ranching economy to an Anglo-dominated farming economy, accompanied by segregation and social change. By the mid-20th century, McAllen evolved into a center for agriculture, oil, and tourism, profoundly influenced by its proximity to Mexico and the discovery of oil in the Reynosa area in 1947.
Economic Impact
The Reynosa McAllen region has evolved into a dynamic economic hub, profoundly impacting both sides of the border.
Maquiladoras
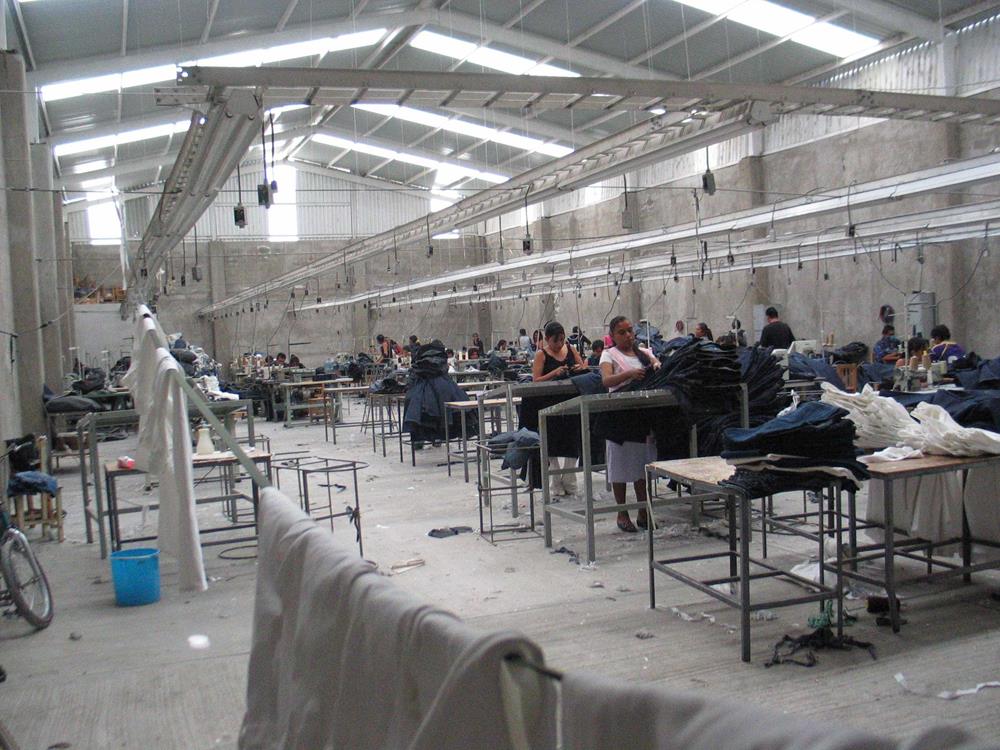
A pivotal element in the region’s economy is the maquiladora industry. Maquiladoras are manufacturing operations in a free trade zone where factories import material and equipment on a duty-free and tariff-free basis for assembly or manufacturing and then re-export the assembled product.
In recent years, the McAllen Economic Development Corporation has collaborated with Reynosa to establish new maquiladoras, attracting significant foreign investment and creating job opportunities. Companies from countries like India, England, and Japan have invested approximately $80 million in the region.
Economic Recovery and Job Growth
The region has shown notable economic progress, underpinned by healthy consumer spending and robust employment growth. McAllen, in particular, has seen a substantial increase in jobs across various sectors, notably in services. The employment surge is a testament to the region’s resilience and capacity for growth, even in challenging economic climates.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the Reynosa McAllen area has seen growth and investment, it has not been without its challenges. Issues such as supply chain disruptions have affected trade values, and the pandemic has significantly impacted both sides of the border. However, lifting travel bans and resuming cross-border travel have provided a much-needed boost to the local economy, particularly in leisure, hospitality, and retail sales.
Cultural Influence
The Reynosa McAllen region, deeply rooted in a rich history, showcases a cultural landscape that’s as diverse as its past.
Early Influences
During the region’s early history, the Spanish colonized the area, establishing settlements and missions along the Rio Grande in the 1700s. These led to the founding of towns like Reynosa and the establishment of religious outposts and ranch settlements in the area. The Spanish settlers, indigenous tribes, and later, American pioneers have interacted and sometimes had conflicts with one another. The blending of these cultures over centuries has significantly shaped the region’s cultural identity.
Modern Cultural Landscape
Today, the Reynosa McAllen area, known as Borderplex, is a melting pot of Mexican and American cultures, being one of the most populous areas on the US-Mexico border. This unique position has made it a focal point for cultural exchange, economic growth, and diversity. The area has experienced rapid urban growth in recent years.
Celebrations and Festivals
The region’s cultural vibrancy is perhaps best showcased in its celebrations and festivals. For instance, McAllen hosts MXLAN, a festival that celebrates Latinx music and arts. This festival is a testament to the region’s diverse cultural influences and its role in bridging the Mexican and American cultures.
Education
The Reynosa McAllen region demonstrates a strong commitment to education, with various initiatives and institutions contributing to its educational landscape.
In McAllen, Texas, the McAllen Independent School District (ISD) showcases impressive academic performance. The district received an overall A rating for the 2021-2022 school year, excelling in student achievement, school progress, and closing performance gaps among different student groups. The graduation rate for students who started ninth grade in 2017-2018 was an impressive 98.4%, well above the statewide average of 90%. Additionally, the dropout rate for grades 9-12 during the 2020-2021 school year was only 0.1%, significantly lower than the state average of 2.4%.
Higher education also plays a crucial role in the region. The Texas A&M University Higher Education Center in McAllen has been pivotal in expanding academic opportunities. The center offers nine undergraduate degree programs, including agricultural economics, biomedical sciences, and public health, emphasizing its dedication to regional development and economic growth.
Across the border, educational partnerships are enhancing opportunities for students in Reynosa. South Texas College has a concurrent enrollment partnership with The Oxford School in Reynosa, providing high school students access to U.S. education and pathways to higher education. This program allows students to earn college credits at a minimal fee, preparing them for American colleges and universities while saving money and time.
Additionally, Texas A&M University is expanding its presence in the region. The groundbreaking of the Texas A&M Health Nursing Education and Research Building at the McAllen campus is scheduled for 2026. This facility will offer programs from the Texas A&M School of Nursing and the School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, emphasizing the commitment to health education and research in the region.
Climate
The climate in the Reynosa McAllen region is characterized by its subtropical nature, with distinct seasonal variations.
Reynosa
In Reynosa, the coldest month is typically January, with average temperatures around 17.0 °C (63 °F). The temperature can drop to around 2.5 °C (36 °F) on colder nights and reach around 31 °C (87.5 °F) during warmer days.
The region experiences minimal precipitation in winter, averaging around 15 mm (0.6 in). As the months progress towards summer, the region becomes significantly hotter. For instance, in June, the average temperature can rise to about 30.3 °C (87 °F), with potential highs around 39 °C (102 °F) and increased precipitation of up to 100 mm (3.9 in) distributed over five days.
McAllen
Similarly, McAllen experiences hot summers and mild winters. The average high temperatures in January, the coldest month, range in the mid-70s F (low 20s C), while in July, the hottest month, they can reach the mid-90s F (high 30s C). The area generally receives limited precipitation, with an annual average of around 22 inches. Notably, McAllen averages 0 inches of snow per year and enjoys approximately 223 sunny days annually.
Tourist Attractions and Experiences in Reynosa-McAllen Region
McAllen, Texas
-
- International Museum of Art & Science (IMAS): A fascinating blend of art and science exhibits catering to both children and adults.
- Quinta Mazatlan: A stunning birding center and Mexican hacienda, perfect for nature lovers.
- McAllen Public Library: Renowned for its innovative approach and community focus, this library offers a wide-array of events and classes for all ages.
- Firemen’s Park and Town Lake: Offers outdoor activities like kayaking, paddle boating, and scenic walks.
- 17th Street Entertainment District: The hub of McAllen’s nightlife, with diverse dining and live music options.
- La Plaza Mall: A premier shopping destination with a variety of stores and eateries.
- McAllen Heritage Center: Learn about the city’s history through interactive exhibits.
- McAllen Performing Arts Center: Hosts a variety of performances and concerts in a state-of-the-art venue.
- McAllen’s Farmers Market: A great spot to find fresh, locally sourced produce and products.
- Downtown McAllen: Explore its shops, galleries, and restaurants, reflecting the local culture and vibrancy.
- Bike around McAllen: Rent a bike and explore the city through its numerous bike paths and trails.
Reynosa, Tamaulipas
- Plaza Principal Miguel Hidalgo: This central park is a great spot to relax and soak in the local atmosphere. It’s a hub for cultural activities and provides a glimpse into the city’s lifestyle.
- Parque Cultural Reynosa: This park serves as both a theater and a park, making it a unique blend of nature and culture. It’s an ideal location for those interested in local arts and performances.
- Plaza Juárez: Another beautiful park in Reynosa, it offers a peaceful environment perfect for a leisurely stroll or a family outing.
- Reynosa Historical Museum (Museo Histórico Reynosa): For those interested in history, this museum, renovated in 1992, offers insights into the rich history of Tamaulipas and the Reynosa area.
- The City of Happy Families: Although temporarily closed, this children’s theme park aims to educate and entertain, allowing kids to learn through play about various professions and skills.
Interesting Facts about the Reynosa-McAllen Region
The Reynosa McAllen region, straddling the US-Mexico border, is rich in cultural, historical, and economic significance. Here are some interesting facts about this unique area:
- The region has historical significance: Reynosa, founded in 1749, was part of Spain’s efforts to colonize the interior of Mexico. It played a role in early rebellions against Spanish rule and has been a site of various historical events, including the Mexican-American War and the Mexican Revolution.
- The site is an economic hub: The region has evolved into a significant economic hub, particularly due to the maquiladora industry in Reynosa. Maquiladoras are manufacturing operations in free trade zones and are pivotal in the region’s economy, contributing significantly to its rapid growth.
- It’s a cultural melting pot: The Reynosa McAllen area is a cultural melting pot, blending Mexican and American influences. This is evident in its festivals, food, and everyday life. The MXLAN festival in McAllen, celebrating Latinx music and arts, is a testament to this cultural vibrancy.
- It’s a strategic location for trade: Its strategic location near the US-Mexico border makes Reynosa an important hub for logistics and transportation companies, enhancing its significance in North American trade.
- There is substantial education and research development: The Texas A&M University Higher Education Center in McAllen and South Texas College’s partnership with schools in Reynosa reflect the region’s commitment to educational development and cross-border academic collaboration.
- Tourism is growing: While not as prominent as other industries, tourism in Reynosa is growing. Proximity to popular tourist destinations like South Padre Island in Texas adds to its appeal. The region also hosts several parks and recreational areas.
- It has a subtropical climate: The region experiences a subtropical climate with hot summers and mild winters, characteristic of the larger Rio Grande Valley area.
Conclusion
The Reynosa-McAllen area is a notable example of cross-border collaboration and economic interdependence. Located in Mexico, Reynosa forms a crucial partnership with McAllen in the United States. Together, they create a bustling economic zone driven by cross-border trade and tourism. This dynamic relationship between the two cities highlights the essential nature of cooperative ties that define many border cities.