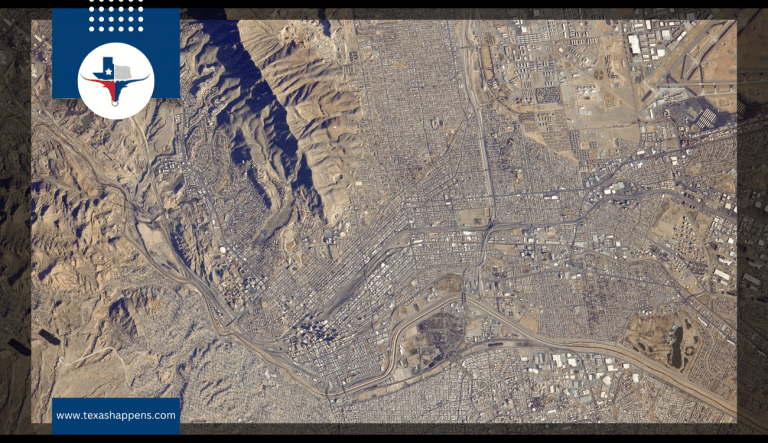
El Paso and Ciudad Juárez form North America’s largest binational community, home to over 3.4 million residents and a thriving $81 billion trade economy. This dynamic region merges manufacturing, education, and culture, with 80% of El Paso’s population identifying as Hispanic and the largest bilingual workforce in the Western Hemisphere. Its deep history and modern innovations highlight a seamless blend of two nations.
Historical Evolution of the Border Region
Long before modern borders, Native Americans thrived along the fertile Rio Grande, where El Paso and Ciudad Juárez now stand. Spanish conquistadors arrived in the 1600s, founding these twin cities and setting the stage for centuries of cultural exchange. Mission Ysleta Texas became a crucial religious and cultural center after its establishment in 1680.
The region’s transformation accelerated after the Texas Revolution and Mexican-American War, introducing border security challenges that persist today. With the arrival of railroads in the late 1800s, it became a vital trade hub, attracting diverse communities and fostering international cooperation. During Prohibition, its strategic location fueled smuggling, reinforcing the complex relationship between these sister cities and shaping their ongoing binational interactions.
Demographics and Cultural Integration
The historical forces that shaped El Paso and Ciudad Juárez have fostered one of North America’s most demographically vibrant metropolitan areas. Over 80% of El Paso’s population identifies as Hispanic, predominantly of Mexican origin, while Ciudad Juárez brings a youthful and energetic presence to the region. Linguistic diversity defines the area’s character, boasting the largest bilingual workforce in the Western Hemisphere and bridging both nations in daily life.
Transnational identities flourish as families, businesses, and cultural practices seamlessly intertwine across the border. This constant exchange of people, ideas, and traditions reinforces the region’s unity, challenging the notion of a strictly divided borderland. This cultural integration mirrors the heritage of cities like Laredo, where Spanish colonial influences have shaped the architectural and cultural landscape since its founding in 1755.
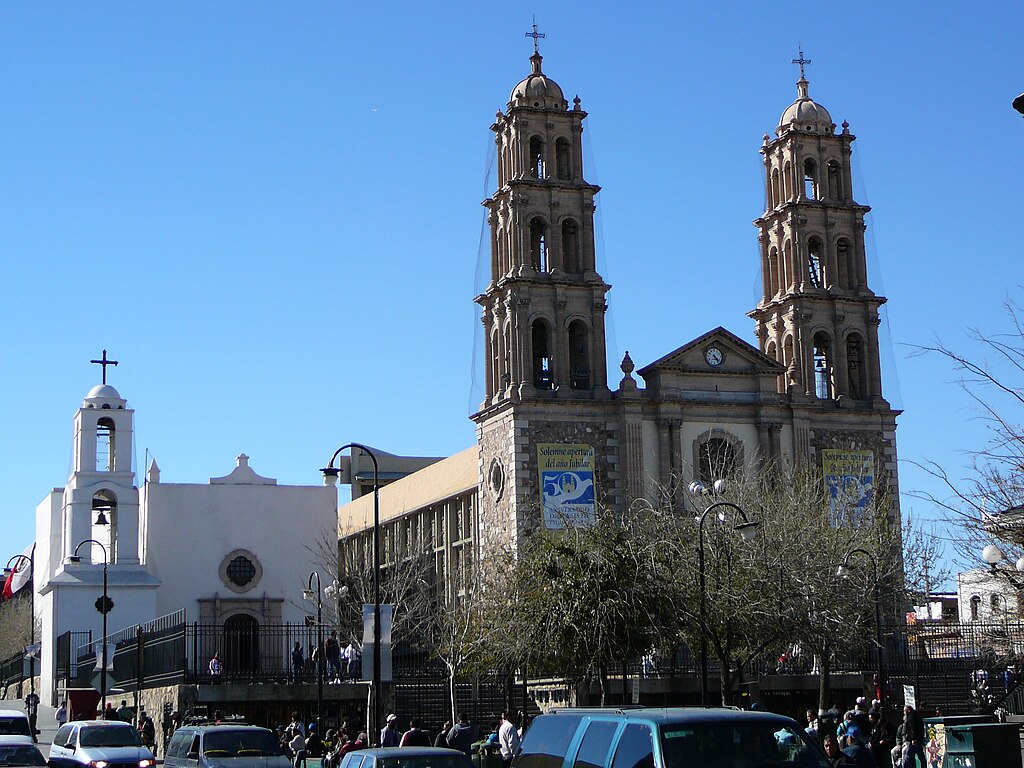

Economic Powerhouse and Trade Relations
Since emerging as a key trade corridor, El Paso-Juárez has evolved into North America’s leading cross-border economic hub, generating over $81 billion in trade in 2018. As the 14th largest trade center in the U.S., its success is driven by deeply integrated supply chains and seamless workforce collaboration across the border.
With more than 320 manufacturing plants and 1,100 operations specializing in automobiles, automotive components, and consumer electronics, the region plays a crucial role in global production. NAFTA significantly expanded Ciudad Juárez’s manufacturing sector, attracting over 70 Fortune 500 companies. Its strategic location and binational workforce continue to reinforce the area’s position as a key force in U.S.-Mexico economic relations.
This economic partnership mirrors the success seen in other border regions, where cities like Acuña have established 55 maquiladora plants operated by major international companies.
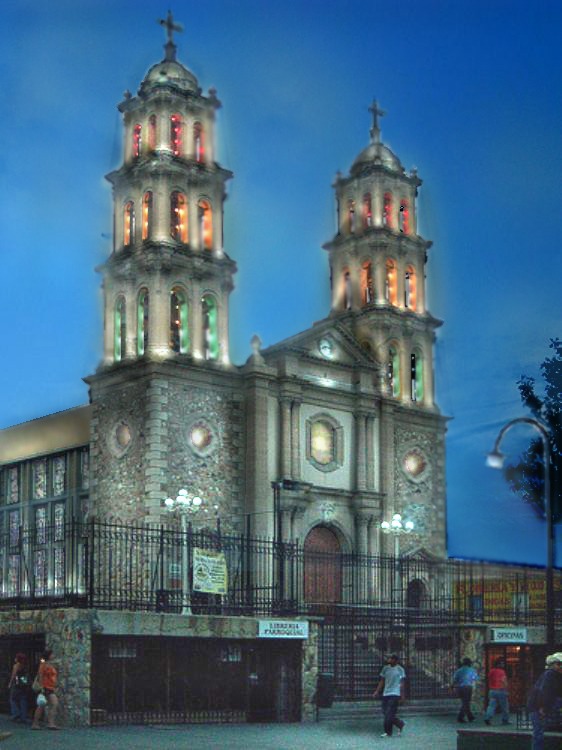

Image: WhoAreS Citizen, Catedral-CJ, CC BY-SA 3.0
Educational Excellence Across Borders
Reflecting the region’s economic energy, a robust network of higher education institutions spans both sides of the border, shaping future binational leaders. UTEP stands at the forefront as a Hispanic-serving institution, offering nearly 170-degree programs and fostering research collaborations with UACJ in Juárez. These partnerships include student exchange programs that enrich the academic experience.
Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso enhances the region’s medical education and research, while NMSU contributes with extensive programs and student success initiatives. The Universidad Tecnológica de Ciudad Juárez further strengthens this cross-border academic ecosystem, making the region a vital hub for learning and innovation. Much like the wide-range education programs that transformed learning at the Houston Museum of Natural Science in 1947, these institutions prioritize accessible education for their communities.
Urban Development and Infrastructure
With a population exceeding 3.4 million, El Paso-Juárez ranks as the second-largest binational metropolitan area along the U.S.-Mexico border. A well-developed network of highways, railways, and two international airports seamlessly connects the two cities, facilitating efficient movement of goods and people.
The region’s infrastructure underpins $81.88 billion in annual cross-border trade, fueling a robust manufacturing sector with over 320 plants and 1,100 operations. Collaborative initiatives like the Paso del Norte Clean Cities Coalition and advanced data networks further enhance regional integration. These advancements have solidified El Paso-Juárez’s position as the 14th largest trade hub in the U.S.

Image: B575, Asia exibit entrance, CC BY-SA 3.0
Arts, Culture, and Community Life
The El Paso-Juárez region thrives with dynamic colors, rhythms, and artistic expression, where Mexican and American influences merge into a distinctive cultural identity. A lively performing arts scene flourishes on both sides of the border, featuring local theater productions, bustling live music venues, and a nightlife filled with energy.
Culinary traditions, shaped by centuries of cultural exchange, offer a rich fusion of flavors, from authentic Mexican street food to contemporary Tex-Mex cuisine. Meanwhile, universities and creative institutions cultivate intellectual growth and artistic innovation, reinforcing the region’s status as a hub of cultural vibrancy and cross-border creativity.
Conclusion
The El Paso-Juárez binational metropolitan area thrives as a unique cross-border community where trade, education, and daily life merge. With a population of over 3.4 million, the region plays a crucial role in U.S.-Mexico relations, generating more than $81 billion in annual trade. Its strong manufacturing sector and strategic location have attracted global businesses, while institutions like UTEP and UACJ cultivate a highly skilled bilingual workforce.
Cultural vibrancy defines the region, blending Mexican and American influences in music, cuisine, and the arts. Local traditions flourish alongside modern urban development, reinforcing a shared identity that transcends borders. As infrastructure expands and binational cooperation deepens, El Paso-Juárez continues to grow as a dynamic, interconnected hub shaping the future of the borderlands.